Technology has greatly expanded the methods of creating, editing, maintaining, transmitting and retrieving records. From creation to disposition, records in electronic recordkeeping systems may now utilize a variety of media. An example of an electronic recordkeeping system is one in which a personal computer generates the original records, which are subsequently stored on a secondary electronic resource. While paper copies of the electronic records may be printed for distribution, the original records are transferred electronically.
Topics: Fraud, Risk Assessment, IT Risk, Strategic Risk, Document Retention, Performance Management/Measurement
How Does Opportunity Risk Apply to Financial Business Processes?
Opportunity risk occurs whenever there’s a possibility that a better opportunity may become available after having committed to an irreversible decision.
We all experience opportunity risk at its most basic level several times a week. For example, imagine you have enough cash on you for lunch in a new town and you’re trying to decide between two restaurants you’ve never tried. What if you spend your time and money on the first option and it’s terrible? Or even maybe it’s not terrible, but the second option is just so much better?
Topics: Risk Assessment, Strategic Risk, Performance Management/Measurement, Budgeting, Cost Management
How Can Human Resource Risk Be Managed?
“All of the blame and none of the praise”
This was how one Human Resource professional described their job in a forum on tech recruiting recently. Human Resources (HR) can be a bit of a mine field full of potential hazards and risks while searching for that perfect candidate to fill a company’s needs.
Topics: Laws & Regulations, Human Resources, Risk Assessment, Strategic Risk, Performance Management/Measurement
How To Minimize Customer Fraud Risk
Fraud is the intentional perversion of truth in order to induce another to part with something of value or to surrender a legal right. In the business community, the ultimate goal of fraud is to gain money. There are numerous frauds within the business world.
Topics: Fraud, Ethics, Risk Assessment, Strategic Risk, Performance Management/Measurement, Customer Satisfaction
What is Organizational Alignment Risk?
What is Organizational Alignment Risk?
Organizational alignment is defined as a conscious and systematic coordination and alignment of three powerful and interrelated driving forces: organizational strategy, organizational culture and organizational infrastructure. Organizational alignment is to be mutually supportive and contribute as efficiently and effectively as possible to meet organizational goals and objectives.
Topics: Enterprise Risk Management, Risk Assessment, Audit Committee & Board, Strategic Risk, Performance Management/Measurement
Process Alignment Risk Key Performance Indicators Guide
What Is Process Alignment Risk?
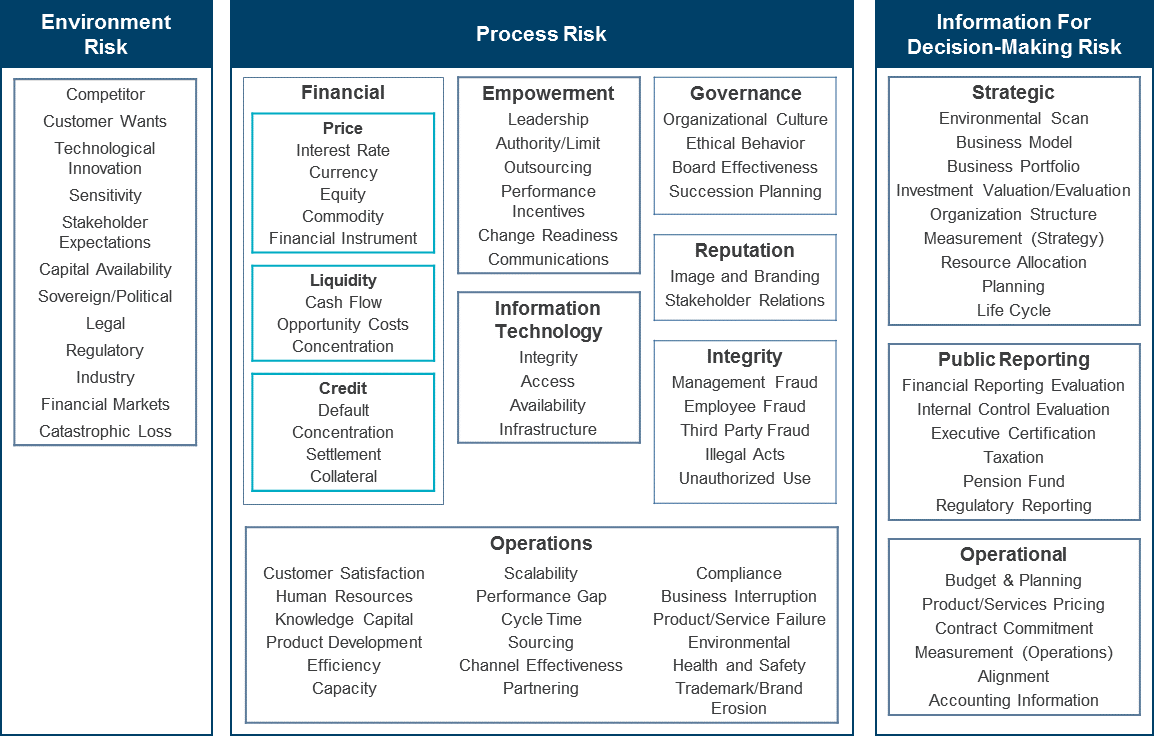
This is the risk that the business processes within a company may not be appropriately aligned with its corporate strategy, resulting in the inability of the organization to meet the demands of its customers efficiently and effectively. Process alignment can be defined as the synchronization of business process objectives and performance measures with organizational objectives and strategies, with a view to avoiding conflicting, uncoordinated activities.
Topics: Risk Assessment, Strategic Risk, Knowledge Management
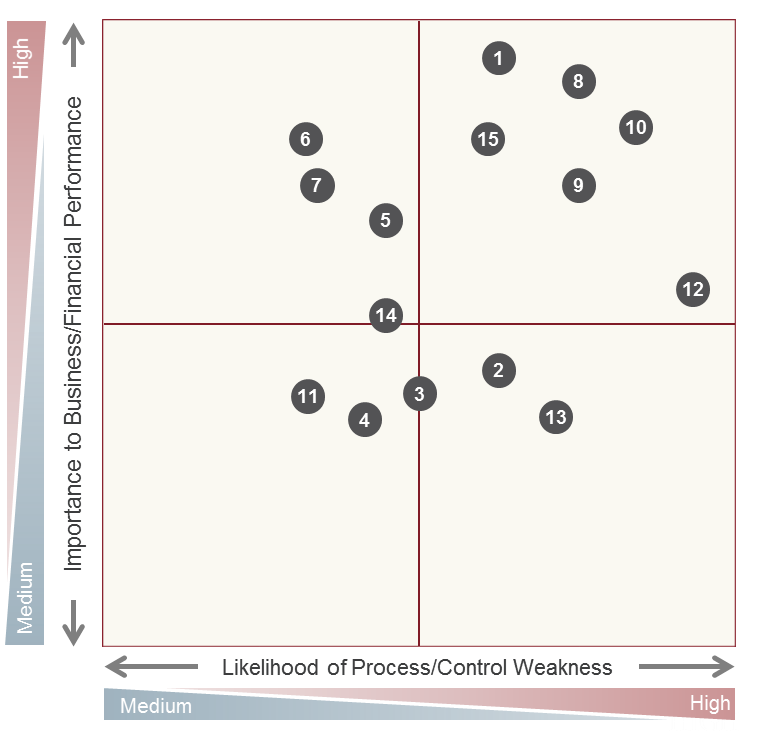
Risk Assessment Maps and Prioritizing Business Processes
Risk assessment helps identify and document critical business processes and the internal controls within each process. Combined with facilitated management meetings, this approach can help gain company-wide consensus by including key process owners in risk and controls analysis.
Topics: Enterprise Risk Management, Risk Assessment, Governance, Risk & Compliance
Guide to Risk and Risk Reporting
Business risk is the level of exposure to uncertainties that the enterprise must understand and effectively manage as it achieves its objectives and creates value. It is not just about threats; there is an upside as well as a downside. Risk is not about a single point estimate—time frame is an important factor when evaluating risk, and exposure and uncertainty are important factors.
Topics: Risk Assessment, Governance, Risk & Compliance, Strategic Risk
Close-the-Books Guide: Reduce Financial Close Risk
A fast, close-the-books process provides multiple benefits for the finance function and for the company. First, a fast close process creates more time for finance professionals to focus on strategic activities for the company, such as identifying warnings in financial data and providing the corporation's financial direction. It also reduces the cost of the finance function, since fewer hours are needed to close the books. And it demonstrates that the company's controls and systems are well organized; the company sends the message to its competitors and to the investment community that it is expert at performing business processes.
Topics: Risk Assessment, Accounting/Finance, Financial Reporting, Close the Books
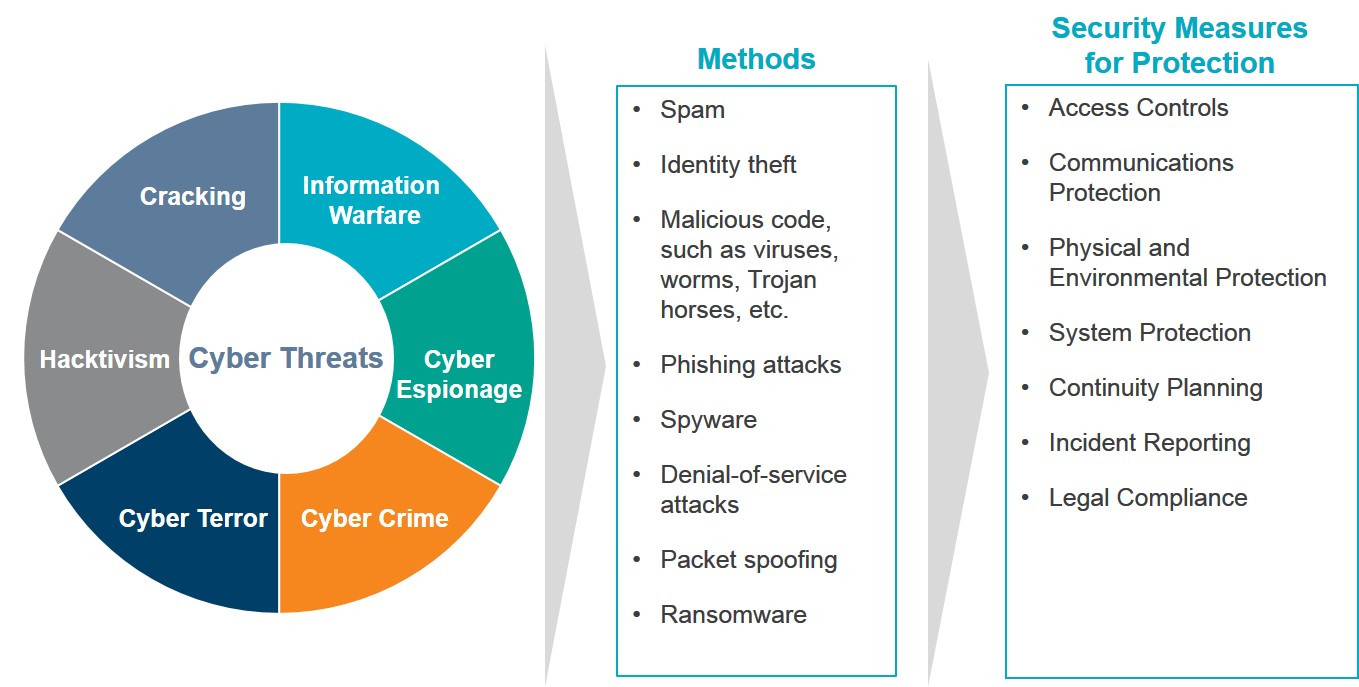
What Is Internal Audit’s Role in Cyber Security?
Corporations today are thinking about how to protect assets. A few of the white collar crime problems include hacking/intrusions (cyber vulnerability), insider/outsider trading (convergence of cyber and financial crimes), the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA), spear fishing (email compromise) and economic espionage. They must consider the possibility of internal corruption or external corruption, and environmental factors such as culture and competition contributing to these crimes. As protection, organizations can use cyber security, pen testing and data loss prevention tactics.
Topics: Enterprise Risk Management, Internal Audit, Internal Controls, Risk Assessment, Cybersecurity, IT Controls
Add a Comment: